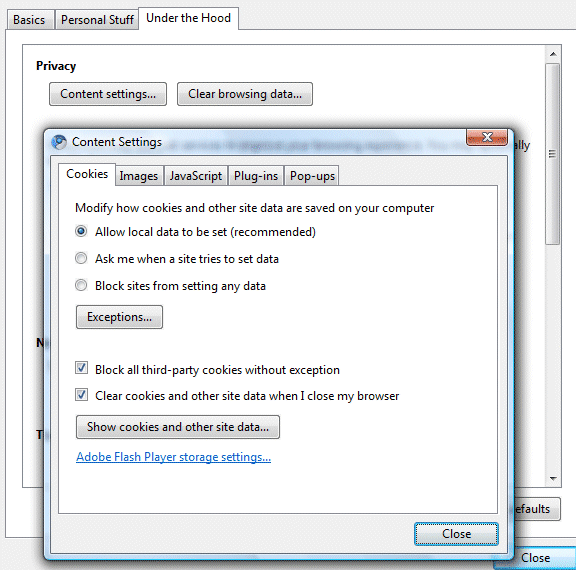
Here are some frequently requested features that are now available if you use the content settings dialog:
1. Disable images - go to the "Images" tab and select "do not show any images". It's a good idea to use this option if you have a slow Internet connection.
2. Disable JavaScript - go to the "JavaScript" tab and select "do not allow any site to run JavaScript". You won't be able to use most web applications, but at least you'll be safer and you won't download unnecessary JavaScript files.
3. Block images from a domain. Make sure that the option "show all images" is enabled, click on "Exceptions" and add a list of domains that aren't allowed to serve images. You might use this option to block ads to or to block images from adult sites.
4. Block scripts from a domain. Make sure that the option "allow all sites to run JavaScript" is enabled, click on "Exceptions" and add a list of domains that aren't allowed to serve scripts. You might use this option to block ads to or to block tracking scripts.
5. Pop-up whitelisting. The default option for pop-ups is to block them, but you can define a list of safe domains that are allowed to show pop-ups. Go to the "Pop-up" tab, click on "Exceptions" and add domains.
6. Block third-party cookies. Now you can block all third-party cookies by enabling the option "Block all third-party cookies without exception" from the "Cookies" tab.
7. Clear cookies when you close the browser. This is a great way to remove tracking cookies, but Chrome's implementation doesn't let you define a list of exceptions. Select "clear cookies and other site data when I close my browser" from the "Cookies" tab to automatically remove cookies and local storage data. Unfortunately, combining cookies and local storage is not a great idea because they're used in different ways.
8. Disable plug-ins. You can disable all plug-ins, including Flash, Java, Windows Media Player or QuickTime if they slow down or crash your browser. Go to the "Plug-ins" tab and select "do not allow any site to use plug-ins". Please note that this feature doesn't disable Chrome extensions.
9. JavaScript whitelisting. It's not as easy to use as the NoScript extension for Firefox, but you can disable JavaScript and only allow a list of trusted domains to use cookies. Go to the "JavaScript" tab, disable JavaScript and a list of exceptions: google.com, yahoo.com and other domains that require cookies to authenticate.
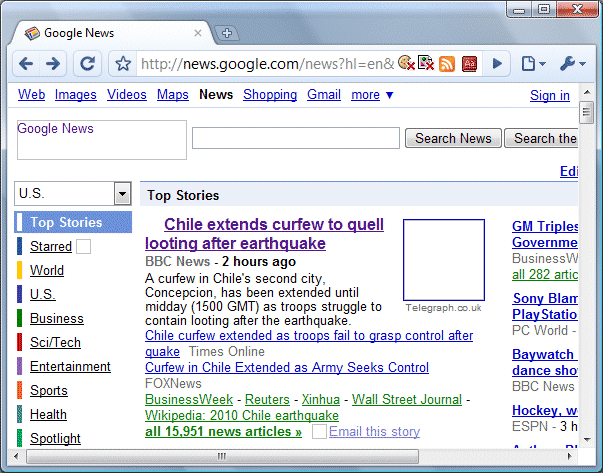
10. Detect blocked content. If you disable images or scripts, Chrome shows some icons inside the address bar which inform you that Chrome blocked content from a page. In most cases, you can add the current site to the list of exceptions and show content from the site. After adding the exception, you need to reload the page to see the changes.
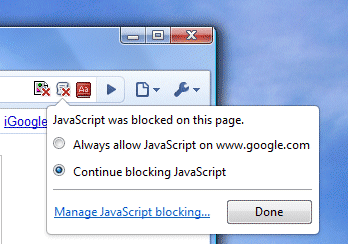
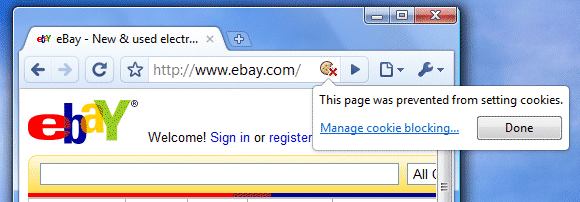
Some missing features that would be useful: defining exceptions for removing cookies when closing the browser, disabling certain plug-ins and disabling animated images.
You can download Chrome 4.1 Beta for Windows from this page. "Content settings" is also available for Linux in the dev channel version of Chrome, but this version is buggier and less polished.
No comments:
Post a Comment